Linux
File System Overview:- Linux
all information is treated as a file. A single disk can store thousands of
files. For organizing data on the disk the operating system provides a file
system. Grouping of similar files together in a structure called directory. The
file system of LINUX is the main key to success and convenience of LINUX
system.
File Type In LINUX
Ordinary
Files / Regular Files:-
All files created by a user come under this category of files. These Include
all data files, program files, object files and executable files. A user can
make changes to such files.
Directory
Files:-
For each directory there is a file by the same name as the directory which
contains information about files under that directory.
Device
Files:-
Device files are special files typically associated with input-output device,
such as printers, tapes, hard-disks, floppy disks etc. The kernel is
responsible for mapping the file names to their respective devices.
LINUX
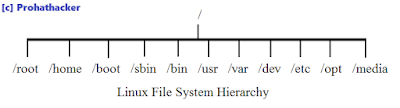
FILE HIERARCHY CONCEPTS
LINUX
follows the tree-structured or hierarchical directory structure. The LINUX file
system is organized as hierarchy that starts with the root directory.
/
- This directory is called as the ‘root’ directory. It is at the top of
the File system structure. All other directories are placed under it.
root
- This
is the default home directory of the root user.
/bin
-
This directory contains executable programs files (binary files). In this
directory, one can find the files for the LINUX commands.
/dev
-
This directory contains the device files. For example the printer may be a file
known as prn, the hard disk may be had file.
/etc - This
directory contains all the system-wide configuration information as text files.
/lib
- This
directory contains the library files. Library files contain the reusable
functions and routines for the programmer to use.
/tmp
- This
directory contains all the temporary files, which will eventually be deleted
from the system. This is similar to C:\windows\temp\ directory in Windows-based
OS.
/mnt
- This
directory contains where the storage devices other than hard disk are mounted.
This directory contains the sub-directories “floppy” and “cdrom”.
/usr
- This
directory contains the home directories of the users, source text for the
online manual (man) pages, games and other directories.
/kernel
- This
directory contains all the kernel-specific code. Kernel is the heart of the
LINUX system. It is responsible for resource-allocation, security and low-level
hardware-interfaces.
/home
- It
contains the home directories of all standard user.
/boot
- It
contains the kernel and also contains the files related for booting the OS such
as boot loader.
/sbin
- sbin
stands for system binary. It contains essential system commands which can only
be used by the superuser.
/var
- var
stands for variable. It contains variable information such as logs files and
print queues.
/media
- It
is the default mount point for removable storage media such as CDROM/ DVD and Pendrive etc.
/opt - opt stands for optional. It generally contains the third party software’s.
/opt - opt stands for optional. It generally contains the third party software’s.
How you liked this article please tell us your thoughts on comment box.

No comments:
Post a Comment